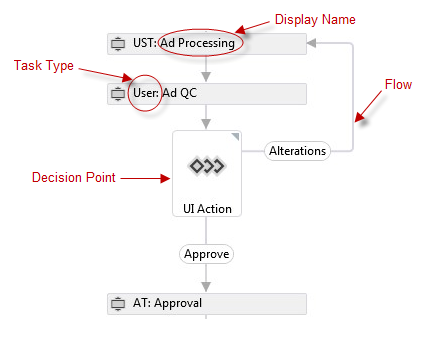
ARTEMIS WorkflowThe sequence of process through which an ad, article, issue, or front and back mater pass from creation to completion. diagrams are standard flowcharts using a ARTEMIS-specific notation.

ARTEMIS automatically opens each task after the previous task closes . Each task must be opened and closed in the order presented in the Workflow, with the exception of Asynchronous Tasks, which are described below. A new task does not open until the preceding task closes.
The User TaskA Task is a function performed by a user. Tasks can contain one or more events. ARTEMIS assigns tasks to a User or Group, but only a User can close a task. is a straightforward task done by an ARTEMIS user. You need to edit the task, interact as necessary (upload a file, for example) and complete the task. For example, most QC tasks such as FreeStyle QC and Comp QC are User Tasks. Some tasks done outside ARTEMIS, such as Copyediting and Editorial Office Corrections, can be User Tasks, in which case, the ARTEMIS user acts on behalf of the outside user by completing the task when it is done.

Email Tasks send emails directly from ARTEMIS to the recipient. User Task Email Tasks (UEU) such as Send Proof and Send File to Copy Editor let you add information in the task screen (such as the name of a copy editor). You then create an email by clicking Create Email and edit it before sending. User Email Tasks (UE) such as FTOC Processing create the email automatically, which you can edit before sending. Email Tasks such as Cover Image Selection create and send an email without user interaction.

All Signal Tasks send eTPThe electronic Transfer Process , an automated method of transferring and tracking files. signals and packages. UST Tasks such as eGalley Composition and Folio let you work with the task, such as uploading a file to send, then send the signal and file package if applicable. These tasks stay open, allowing you to send another signal (such as an additional file) and only close when ARTEMIS receives the final eTP signal from the vendor. ST Tasks such as ELD Processing send signals automatically when a task is opened, requiring no user interaction. USU Tasks, such as Files to Printer TK.

Userless Tasks such as MS Prep and Graphics Processing are vendor tasks that open and close in response to Signal (eTP) tasks.

Asynchronous tasks open when a preceding task closes; the workflow can continue even when these tasks remain open. AsyncT Tasks such as Graphic Processing have a corresponding Await Task later in the workflow. AsyncU Tasks such as CE Invoice Received are User Tasks that can be closed at a later date. When these tasks are open, they may have an Awaiting Vendor Status.

All Automated Tasks are opened without user input either in communication with a system (such as The Author Center(TAC) A browser-based, automated interface for authors to deliver, retrieve, correct, and return proofs. or a previous ARTEMIS Task), or in response to an eTP signal task. Generally, they indicate a process is taking place outside ARTEMIS.
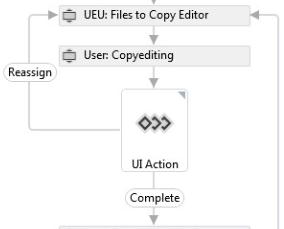
Decision points drive the workflow based on input. UI Action indicates a user button choice in a Task screen; the button choices (for example, Alterations and Approve) are always listed in the Workflow. Prop gets a property value from a component or a Task screen, such as CompType, or a Task screen selection, such as a Figure Corrections value of Y, R, or N.
Interpreting WorkflowThe sequence of process through which an ad, article, issue, or front and back mater pass from creation to completion. Diagrams.htm | Copyright © 2015 Dartmouth Journal Services All Rights Reserved.